Orthogonal Site-Specific Dual Bioconjugation of Aryl and Alkyl Thiols
M.A.R. de Geus MAR; C.E. Stieger; J.V.V. Arafiles; J.P.J. Lotthé; P. Schmieder; K. Kemnitz-Hassanin; B. Kindt; H. Leonhardt; S. Schmitt; H. Gerlach; D. Schumacher; J. Helma; M.A. Kasper; C.P.R.Hackenberger
J.Am.Chem.Soc 168, 18888 - 18900 (2025)
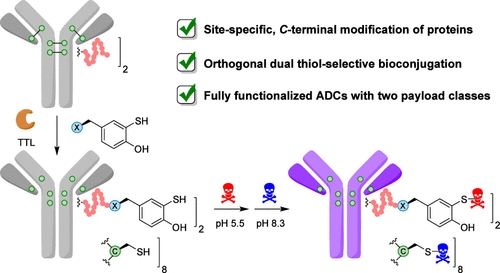
We introduce aryl thiols as nucleophiles for site- specific protein and antibody bioconjugation, which allows the orthogonal labeling of native cysteines for double modification strategies. In a high-yielding synthesis, we introduce aromatic thiol substituents in two amino acids (4-SH-L-Phe and 3-SH-L-Tyr), which can be site-specifically incorporated into the C-terminus of a protein using the enzyme tubulin tyrosine ligase (TTL, Tub-tag labeling). In particular, we found that 3-SH-L-tyrosine shows excellent water solubility and incorporation rates, similar to previously described Tyr-derivatives. 2D NMR experiments revealed a pKa value of 5.5 for the aryl thiol modality of 3-SH-L- tyrosine, which matches the pH-dependent reactivity profile toward thiol-selective ethynyl-triazolyl-phosphinate (ETP) electro- philes. Most importantly, we found that the addition of glutathione had no significant effect on the reaction between ETPs and the aryl thiol at pH 7.0 and below, supporting orthogonal reactivity between the aryl and alkyl thiols. We utilized these findings to develop an orthogonal thiol-selective dual bioconjugation protocol for proteins, featuring TTL-ligation to site-specifically incorporate the arylthiol-containing amino acid derivative, followed by aryl thiolate functionalization at pH 5.5 and subsequent conjugation of cysteines at pH 8.3. This dual bioconjugation strategy was used to generate a highly fluorescent photostabilized nanobody and a fully functionalized antibody-drug conjugate carrying two different cytotoxic payloads, which displays potent cytotoxicity toward cells carrying the target antigen in addition to a strong bystander effect.
